Metabolic Syndrome and Inflammation
 Understanding Inflammation and Its Chronic Impact
Understanding Inflammation and Its Chronic Impact
The Inflammatory Process
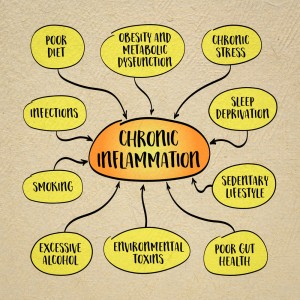
Inflammation is the body’s defense mechanism against harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, toxins, and injuries. In acute inflammation, these responses are typically self-limiting and resolve once the offending agent is removed. However, when inflammation persists, it becomes chronic, leading to tissue damage and a heightened risk of various diseases.
Chronic Inflammation and Disease
Chronic inflammation has been implicated in a wide range of conditions. For instance:
Arthritis: Persistent joint inflammation can lead to pain, stiffness, and progressive joint damage.
Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic inflammatory processes can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (plaque build-up in arteries), increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes: Low-grade inflammation is a common feature in metabolic disorders, adversely affecting insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism.
Autoimmune Disorders: Autoimmune conditions involve dysregulated immune responses that result in chronic inflammation. An example is eczema.
Given the central role of inflammation in these chronic conditions, anything that will lessen the inflammatory response has the potential to improve health outcomes.
Foods that Can Support Lower Inflammation
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and olive oil can lower your overall inflammation levels.
Camel Milk: A Super Food that Can Help Support Lower Inflammation
Camel milk has been consumed for centuries in arid and semi-arid regions due to its nutritional value and health benefits. A natural product, camel milk is a nutritional powerhouse with a high content of proteins, vitamins, lipids, amino acids, and minerals.
Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Camel milk has anti-inflammatory properties. In particular, lactoferrin, found in camel’s milk, has strong antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Camel milk also contains immunoglobulins and lysozyme, which contribute to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
There is scientific evidence, numerous studies, and clinical trials supporting the role of camel milk in lessening chronic inflammation. This evidence shows how camel milk can serve as valuable help in the management of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Bioactive Compounds in Camel Milk
Several components of camel milk are believed to contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects:
Immunoglobulins: Camel milk contains a unique spectrum of immunoglobulins, which play a role in modulating immune responses and may help reduce excessive inflammation.
Lactoferrin: Lactoferrin has been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory compounds and to promote anti-inflammatory pathways.
Bioactive Peptides: During digestion, proteins in camel milk are broken down into smaller peptides, some of which exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties. These peptides can inhibit inflammatory enzymes and modulate cellular responses to stress.
Vitamins and Minerals: Camel milk is rich in vitamin C, B-complex vitamins, zinc, and selenium. Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, helps to neutralize free radicals, while zinc and selenium are essential for the proper function of immune cells. These micronutrients play a supportive role in reducing oxidative stress, which is closely linked to chronic inflammation.
Fatty Acid Profile: The lipid composition of camel milk includes a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids compared to cow milk. Unsaturated fats are known to have anti-inflammatory effects by influencing cellular membrane fluidity and signaling pathways.
So, camel milk could be considered a valuable nutritional addition to an anti-inflammatory diet.
Want to try Camel Milk? Try 2 Packets for 24% Off & Free Shipping (Go to Shop to Order)
Learn more and Order Camel Milk
STILL HAVE QUESTIONS? EMAIL AND GET YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED.
Sign up to receive the MCVitamins Newsletter!
Up-to-date info on the latest health-related news happening in the world
(available in English only)

