Acupuncture and Acupressure – Traditional Chinese Medicine
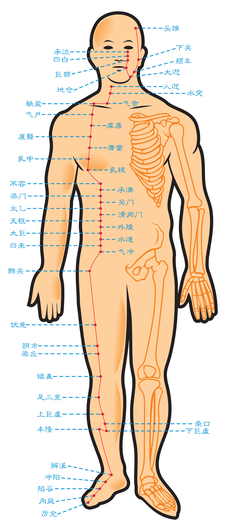 What is Acupuncture?
What is Acupuncture?
Acupuncture is an ancient healing art that has been used for more than 2500 years. It is part of Traditional Chinese medicine for healing the body.
Acupuncture in Chinese is known as Zhen Jiu and Acupressure is Zhi Ya. These flourished in Asia until western medicine was introduced in the 17th century.
Acupuncture and Acupressure started making a comeback in the late 1920s and in 1970s was recognized by the World Health Organization as an effective method of treating 40 major internal diseases.
How does Acupuncture and Acupressure work?
It is based on the idea that there are more than 2000 points on the body which are connected by pathways called meridians. Meridians in Chinese medicine are paths through which the life-energy flows. This energy circulates throughout the body along these well defined pathways. These pathways are connected to specific organs, body structures and systems.
Acupuncture seeks to release the flow of the body’s vital energy or “chi” by stimulating points along 14 energy pathways.
If this energy circulation is blocked, the disruption of this energy flow blocks optimum function in the body, and this results in pain or illness. This disruption of energy can lead to imbalances and chronic disease.
The treatment involves stimulating these points to balance the circulation of energy which influences the health of the entire body.
Scientists say the needles cause the body to release endorphins — natural painkillers — and may boost blood flow and change brain activity. This sounds like medicine not being able to understand acupuncture so going back to their “brain chemical” theory which cannot be proven.
Acupuncture Treatment
Acupuncture involves the insertion of metallic hair-thin needles (3 – 15 of them) into the specific acupuncture points that affect the unhealthy part of the body. It generally involves little or no discomfort, and patients often say they feel energized or relaxed following the treatment.
Acupuncture is used on a number of chronic health conditions.
Acupressure
Closely related to acupuncture and both rely on the same fundamental principles and both the same points and meridians. Acupressure is the use of pressure on the acupuncture points. The term acupuncture is often used to describe all of these as they have similar benefits.
Traditional acupuncture involves the use of needles but the stimulation of acupuncture points is done in acupressure with hands and small devices.
Acupressure uses hands and pressure to stimulate specific key points on the body. Acupressure can be used for many things including acupressure to induce labor to induce menstruation and acupressure for weight loss.
Acupressure differs due to the ability of self-practice. You can learn to practice on yourself.
Another explanation by medicine
One explanation is that both acupuncture and acupressure stimulates your central nervous system to release natural chemicals that alter bodily systems, pain and other biological processes. It can stimulate and perhaps release immune system cells or pain-killing chemicals. It can activate the body’s natural pain handling system. It can stimulate the glands which modulate the body’s systems or it can change the secretion of neurotransmitters which can positively influence the brain chemistry.
Acupuncture Has 30 Proven Uses and 60+ Potential Uses
One of the most common uses is treating chronic pain. One analysis shows that acupuncture has a clear effect in reducing chronic pain, even better than standard drug-based pain treatment and without side effects.
The study showed that the participants averaged a 50% reduction in pain while the drug treatment had a 28% pain reduction.
Extensive review and analysis of clinical trials related to acupuncture, and reported the procedure has been proven effective for the following diseases:
- Adverse reactions to radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy
- Allergic rhinitis (irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose) including hay fever
- Biliary colic – a type of pain related to the gallbladder that occurs when a gallstone transiently obstructs the cystic duct
- Depression (including depressive neurosis and depression following stroke)
- Dysentery, acute bacillary – the most common and violent form of dysentery, caused by bacteria.
- Dysmenorrhoea – Painful periods
- Epigastralgia, pain in the upper abdomen (in peptic ulcer, acute and chronic gastritis, and gastrospasm)
- Facial pain (including craniomandibular disorders)
- Headache
- Hypertension, and Hypotension
- Induction of labor
- Knee pain
- Leukopenia (low white blood count)
- Low back pain
- Malposition of fetus (fetus in wrong position)
- Morning sickness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neck pain
- Pain in dentistry (including dental pain and temporomandibular dysfunction)
- Periarthritis of shoulder – inflammation of the structures (as the muscles, tendons, and bursa of the shoulder) around a joint
- Postoperative pain
- Renal colic – the severe pain produced by the passage of a stone from the kidney through the ureter on the way to the bladder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sciatica
- Sprain
- Stroke
- Tennis elbow
One study on acupuncture for cancer patients suffering from nausea during radiotherapy, 95 percent of the patients felt that the treatment helped relieve nausea, and 67 percent experienced other positive effects such as improved sleep, brighter mood, and less pain.
Additionally, acupuncture has also shown a therapeutic effect for treating the following diseases and conditions:
- Abdominal pain (in acute gastroenteritis or due to gastrointestinal spasm)
- Acne vulgaris – a chronic acne involving mainly the face, chest, and shoulders that is common in adolescent humans and various domestic animals and is characterized by the intermittent formation of lesions often resulting in considerable scarring
- Alcohol dependence and detoxification
- Bell’s palsy
- Bronchial asthma
- Cancer pain
- Cardiac neurosis – a condition marked by shortness of breath, fatigue, rapid pulse, and heart palpitation sometimes with extra beats that occurs chiefly with exertion and is not due to physical disease of the heart—called also cardiac neurosis, effort syndrome, irritable heart, soldier’s heart
- Cholecystitis – inflammation of the gallbladder
- Cholelithiasis – production of gallstones; and he resulting abnormal condition
- Competition stress syndrome
- Craniocerebral injury, involving both cranium and brain
- Diabetes mellitus, non-insulin-dependent
- Earache
- Epidemic haemorrhagic fever – characterized by acute renal failure in addition to the usual symptoms
- Epistaxis – infection
- Eye pain
- Female infertility
- Facial spasm
- Female urethral syndrome – a group of symptoms (as urinary frequency and urgency, pain and discomfort in the lower abdominal region, and dysuria) that resemble those of a urinary tract infection but for which no significant bacteriuria exists
- Fibromyalgia and fasciitis (inflammation of the connective tissue)
- Gouty arthritis Hepatitis B virus
- Herpes zoster
- Hyperlipaemia – the presence of excess fat or lipids in the blood
- Hypo-ovarianism – a condition marked by a deficiency of ovarian function
- Insomnia
- Labor pain
- Lactation, deficiency of
- Male sexual dysfunction
- Ménière disease
- Neuralgia
- Neurodermatitis – chronic dermatitis arising from repeated rubbing or scratching of a real or imagined irritation of the skin
- Obesity
- Opium, cocaine and heroin dependence
- Osteoarthritis
- Pain due to endoscopic examination
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (Stein-Leventhal syndrome)
- Postoperative convalescence
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Prostatitis
- Pruritus
- Radicular (nerve root) pain syndrome
- Raynaud syndrome
- Recurrent lower urinary-tract infection
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
- Retention of urine, traumatic
- Sjögren syndrome
- Sore throat (including tonsillitis)
- Spine pain, acute
- Stiff neck
- Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
- Tietze syndrome – inflammation of costochondral cartilage
- Tobacco dependence
- Tourette syndrome
- Ulcerative colitis
- Urolithiasis – a condition that is characterized by the formation or presence of calculi (stones) in the urinary tract
- Vascular dementia – dementia (as multi-infarct dementia) of abrupt or gradual onset that is caused by cerebrovascular disease
- Whooping cough (pertussis)
Acupuncture and Acupressure is also felt to enhance overall health.
RECOMMENDED:
Acupressure for Stress and improving health
Learn how to do acupressure on yourself using Dr. Berg specially designed device. This invention makes it easy to reduce stress, get into the best sleep of your life and other health benefits.
Use it as a tripod to address different stress points on your body.
Complete Program Includes 12 Step-by-Step Video Tutorials
Dr. Berg’s Acupressure Device – more information, reviews and videos by Dr. Berg to explain more.
Go to and Order Dr. Berg’s Acupressure Device
STILL HAVE QUESTIONS? EMAIL AND GET YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED.
Sign up to receive the MCVitamins Newsletter!
Up-to-date info on the latest health-related news happening in the world
(available in English only)

