Spinal Stenosis, what is it?
The spine is made up of 33 bones. These bones and the spinal discs between them provide a passage for the spinal cord and nerves. The spinal cord itself connects the nerves of the body to the brain. The spinal cord is a long, tube-like structure that conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain.
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of areas in the back or the neck, which causes pressure on the spinal cord or one or more of the spinal nerves.
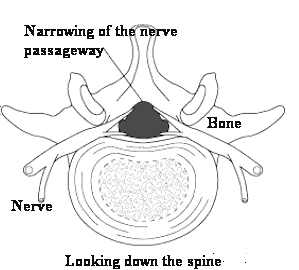
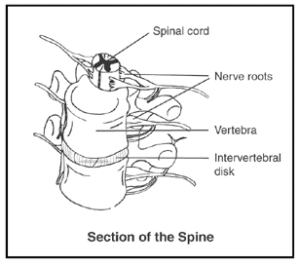
Stenosis can affect any part of the spine, although it rarely affects the upper back. When the narrowed area is in the bones of the neck, it is called cervical stenosis.
When the narrowed area is in the bones of the lower back, it is called lumbar stenosis.
In people with spinal stenosis, the spine is narrowed in one or more of three parts:
- The space at the center of the spine
- The canals where nerves branch out from the spine
- The space between vertebrae (the bones of the spine).
Symptoms
- Numbness, cramping, or pain in the back, buttocks, thighs, or calves, or in the neck, shoulders, or arms
- Weakness of a portion of a leg or arm
- Symptoms will gradually worsen over time. Most often, symptoms will be on one side of the body or the other.
Symptoms are more likely to be present or get worse when a person stands or walks. The symptoms will often lessen or disappear when a person sits down or leans forward. Most people with spinal stenosis cannot walk for a long period of time.
More serious symptoms include:
- Difficulty or imbalance when walking
- Problems controlling urine or bowel movements
- Problems urinating or having a bowel movement
Spinal stenosis may be caused by:
- Arthritis involving the spine, usually in middle-aged or elderly people.
- Two forms of arthritis may affect the spine: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Herniated or slipped disk
- An injury that causes pressure on the nerve roots or the spinal cord itself
- Defect in the spine that was present from birth (congenital defect)
- Paget’s disease of bone – Paget’s disease of bone, the rate at which old bone is broken down and new bone is formed becomes distorted. Over time, the affected bones may become fragile and misshapen.
Other causes of spinal stenosis are:
- Tumors of the spine
- Injuries
- Too much fluoride in the bodyCalcium deposits on the ligaments that run along the spine
- Achondroplasia – a disorder of bone growth that causes the most common type of dwarfism.
Treatments
Medical Treatments:
Generally, conservative medical management involving the use of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes is prescribed. Steroid injections may relieve pain for a period of time.
Various other medications are used for chronic pain, including anticonvulsants phenytoin & carbamazepine, or tricyclic antidepressants.
If the pain is persistent and does not respond to these measures, medical doctors will consider surgery to relieve the pressure on the nerves or spinal cord. Surgery is performed on the neck or lower back, depending on the site of the nerve compression.
Surgery: The most common surgical procedure for spinal stenosis is a laminectomy. The term is derived from two words: lamina (part of the spinal canal’s bony roof) and -ectomy (removal).
The object of a laminectomy is to remove the pressure on the nerve root. The pressure is the cause of the pain and other debilitating effects of stenosis. The surgery can be performed using traditional or microsurgical techniques. The surgeon removes bone and debris from the opening through the bone to reduce pressure on the nerve root.
Recovery is the process that requires a gradual but persistent effort to increase physical strength and minimize weaknesses
Problems with Surgery
A prevalent problem with spinal surgery is nerve damage. Most often, the surgeon feels this will go away in time, but it may not, and can be painful for the patient. Medical doctors will prescribe anti-convulsants and anti-depressants.
See Neuropathy (Nerve Damage) from Surgery
Want to Know More About Neuropathy?
Neuropathy Information Hub
Natural Treatments
Acupuncture/Acupressure – Using Chinese medicine theory, acupuncture and acupressure have been shown to be successful in the reduction of pain
Chiropractic – Chiropractic manipulation will help to realign the spine and reduce the stress on the spinal column and nerves. Chiropractors may also use ultrasound stimulation, nutrition, and exercise in their treatment regimen.
Cranial-Sacral Therapy can be very effective in easing the pressure and pain on the cervical spine. It involves light touching that helps to balance the cranial-sacral system and is often used in alleviating back pain.
Swedish Massage – Traditional Swedish massage can be very effective in the reduction of pain caused by spinal stenosis
Physical therapy and/or prescribed exercises to maintain motion of the spine and build endurance, which helps stabilize the spine.
Supplements
If the body is building up calcium deposits, which are causing the bone to become thicker in the center of the spine or space between the vertebrae, moving the calcium may help.
Vitamin F
In order for calcium to be used by the body, it needs vitamin D to absorb it and Vitamin F to move it around. If Vitamin F is not present, the calcium remains in the joints, blood vessels, etc. It can also thicken bone in all the wrong places.
Where can you get Vitamin F? Essential fatty acids –
Vitamins F, an essential fatty acid, is composed of two fatty acids—linoleic acid (LA) and alpha-linoleic acid (LNA)—with linoleic acid being the most complete fatty acid.
There are two basic categories of EFAs (essential fatty acids)—omega-3 and omega-6—which include linoleic acid and gamma-linoleic acid.
Omega 6 is commonly gotten from the food we eat, including vegetable oil, salad dressing, mayonnaise, nuts & seeds, chicken, beef, pork, dairy products, eggs, and even fast food has Omega 6.
But for Omega-3, we suggest Omega-3 Fish Oil.
We recommend Cold Water Fish Oil. When the fish comes from deep, cold waters, it doesn’t have pollutants.
For more information about Fish Oil
Sign up to receive the MCVitamins Newsletter!
Up-to-date info on the latest health-related news happening in the world
(available in English only)

